Easy Notecards These Vessels May Be Continuous or Fenestrated
1
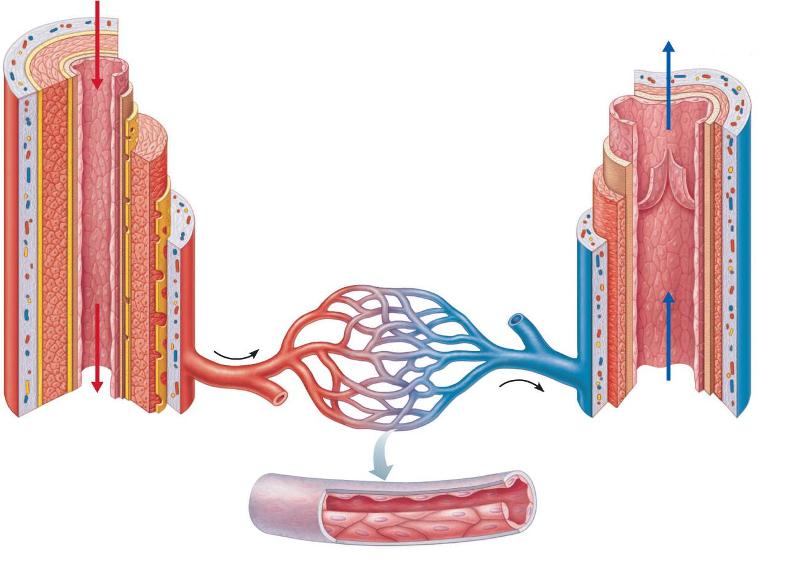
delivery system of dynamic structures that begins & ends at the heart
carry blood away from heart
3
_____ arteries carry deoxygenated blood
small arteries that empty into capillary beds
contact tissue cells + directly serve cellular needs
*exchange vessels
carry blood towards heart
small veins that drain capillary beds
8
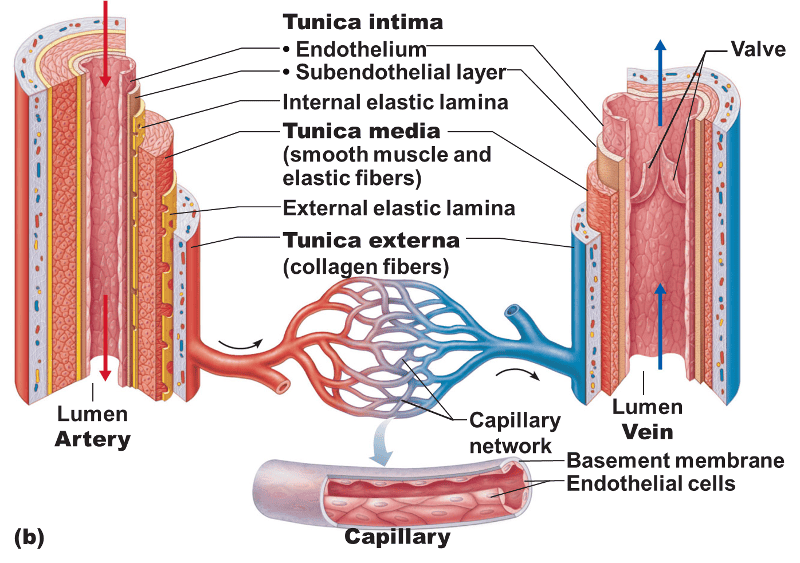
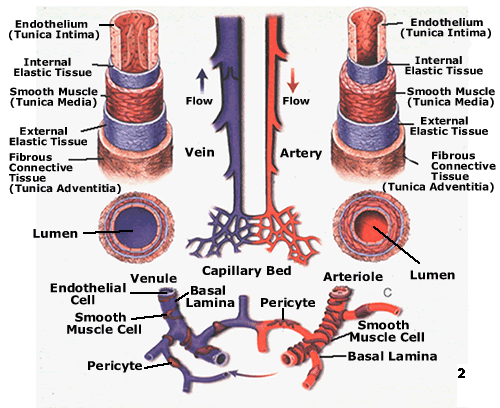
Arteries + veins have 3 layers (tunics)
central blood containing space
endothelium (layer of simple epethelium) with sparse basal lamina
12
inner lining of tunica intima
has direct contact with blood as it flows through the lumen
*lined with endothelium
13
basement membrane of tunica intima
deep to the endothelium that provides physical support for the epithelial layer
*contains collagen fibers + provides tensile strength
14
elastic lamina of tunica intima
elastic fibers that give vessels stretch + recoil properties
smooth muscle + sheets of elastin
sympathetic vasomotor nerve fibers control vascoconsrtiction + vasodilation of vessels
most variable of the tunics
16
tunica externa (tunica adventitia)
consists of collagen + elastic fibers
larger vessels contain vasa vasorum to nourish the external layer
small vessels that supply blood to the tissues of the cells
18
tunica intima consists of
endothelium
subendothelial layer
internal elastic lamina
19
tunica media consists of
smooth muscles + elastic fibers
21
*conducting arteries
act as pressure reservoirs- expand and recoil as blood is ejected from the heart
propel blood onward while ventricles are relaxing
23
elastic arteries have ____ luman which offer ___-resistance
lie distal to elastic arteries
*deliver blood to body organs
***aka distributing arteries
25
muscular arteries have thick ____ ____ with more smooth muscle
union of 2+ arteries supplying the same body region
provide alternate routes for blood to reach a tissue/organ
referred to as collateral circulation
smallest arteries that lead to capillary beds
plays a key role in blood flow regulation from arteries into capillaries by regulating resistance
changes in diameter causes changes in blood pressure
28
the tunica media of _______ consists of a layer of smooth muscle which controls flow into capillary beds via ____ + ____
artioles; vasodilation + vascoconstriction
has thin tunica intima
its large surface area provides rapid exchange of material
found in all tissues except cartiledge, epithelia, and the cornea + lens of the eye
30
the thin tunica _____ of the ____ allows passage of only a single RBC at a time
31
3 structural types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoidal
most; abundant in skin + muscles
33
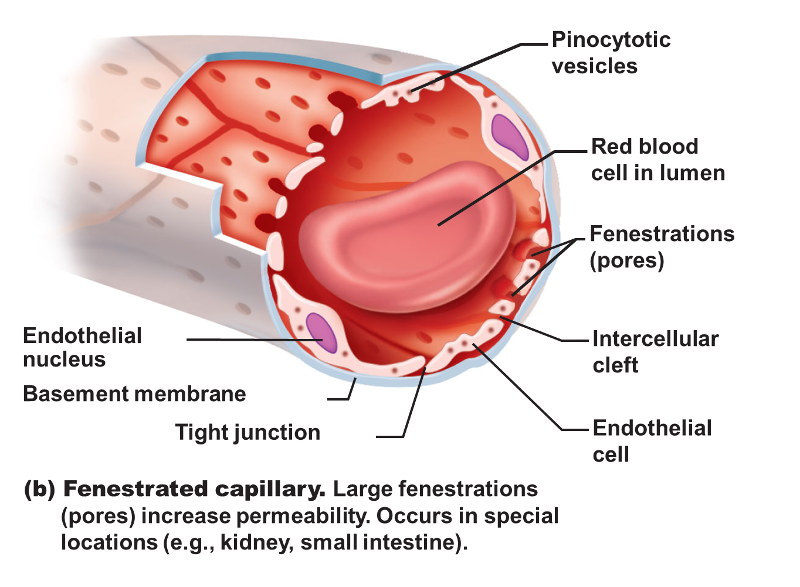
fenestrated capillaries
porous; found in kidneys, villi of s. intestine, choroid plexuses of brain ventricles, ciliary processes of the eyes & most endocrine glands
34
continuous capillary
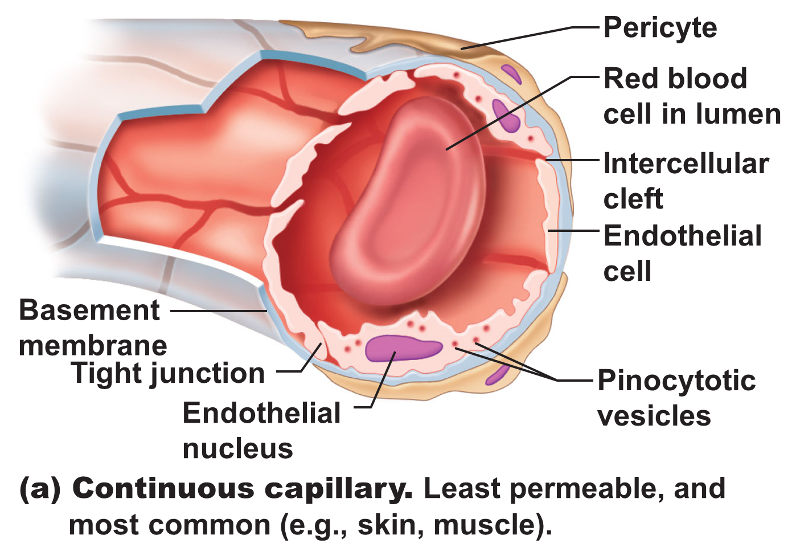
35
fenestrated capillary
36
sinusoidal
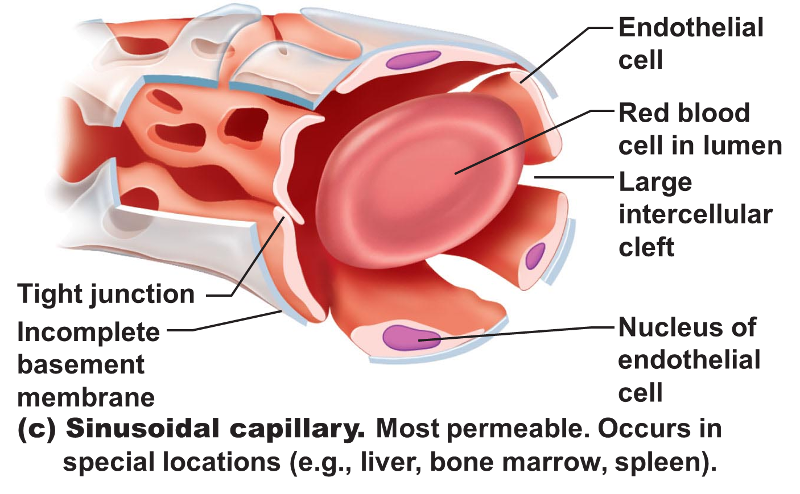
formed when capillary beds unite
very porous; allow fluids + WBC's into tissues
post-capillary venules consist of endothelium and a few pericytes
converge to form veins
38
larger venules have 1-2 layers of
serve as blood reservoirs- contain up to 65% of the blood supply at rest
40
structural features of veins
thinner walls + larger lumens than arteries
thin tunica media and thick tunica externa consisting of collagen fibers and elastic networks
valves
structural modifications of the endothelial lining that aid venous return
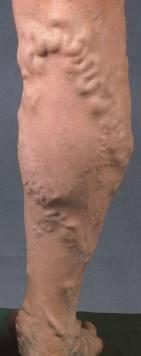
leaky venous valves that cause veins to become dilated & torturous
43
capillary exchange: substances enter and leave capillaries in 3 ways
1. simple diffusion
2. trancytosis
3. bulk flow
*solute exchange between blood + tissues;
molecules and solutes move from an area of high to low concentration
vesicular transport for large, lipid-insoluble molecules that can't diffuse simply
large #'s of ions, molecules, particles in a fluid move together in the same direction
pressure driven filteration + reabsorption
regulates relative volumes of blood & interstitial
pressure-driven movement of fluid + solutes from blood capillaries into interstitial spaces
48
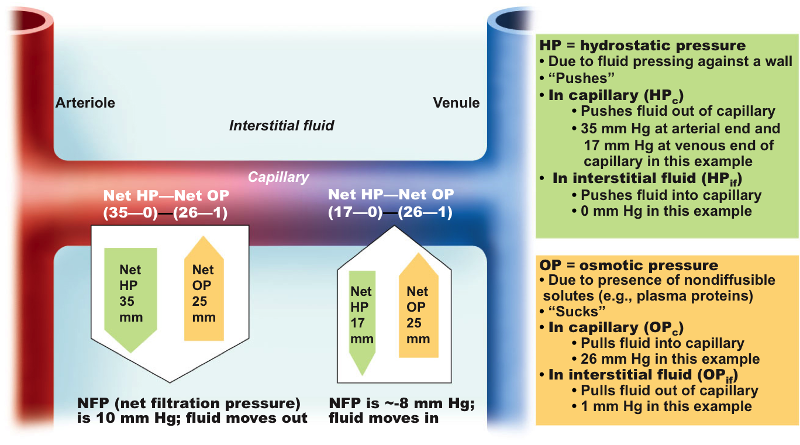
pressures promoting filtration
blood hydrostatic (pumping action of the heart)
interstitial fluid osmotic pressure
pressure-driven movement of fluid + solutes from interstitial spaces to blood capillaries
50
pressure promoting reabsorption
blood colloid osmotic pressure
51
net filteration pressure
balances filtration + reabsorption
52
starling's law of the capillaries
equilibrium maintained between pressure driven filtration + pressure driven reabsorption
*determines whether volume of fluid & solutes reabsorbed matches the filtered-volume
53
Net Filtration Pressure =
NFP= (BHP + IFOP) - (BCOP + IFHP)
54
Blood hydrostatic pressure (BHP)
result of pressure that water in blood plasma exerts against vessel walls
*35 mmHg
-pushes fluid out of the capillaries into interstitial fluid
55
interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure (IFOP)
opposes BHP
* close to 0 mmHg
-pushes fluid from interstitial spaces back into capillaries
56
blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)
force caused by colloidal suspension of large plasma proteins
*26 mmHg
-Pulls fluid out of the interstitial fluid into capillaries
57
Interstitial fluid osmotic pressure (IFOP)
Opposes BCOP
Approximately 0.1-5 mmHg
Pulls fluid out of capillaries into interstitial fluid
*Usually only a small amount of protein here because most of it is taken up by the lymphatic system
NFP = about 10 mmHg at the arterial end of a capillary so that there is a net outward pressure and fluid moves out of the capillary and into interstitial spaces
NFP = -9 mmHg at the venous end of the capillary so that there is a net inward pressure and fluid moves into the capillary from the tissue spaces
85% of fluid filtered out of the capillaries is reabsorbed
60
NFP: Excess enters ______ and is returned to the jugular and subclavian veins in the
lymphatic system; upper thorax
61

62
vasquezwhoust1944.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/11327
0 Response to "Easy Notecards These Vessels May Be Continuous or Fenestrated"
Post a Comment